Understanding Fuel Level Sensors
Fuel level sensors play a critical role in monitoring fuel levels within vehicles, especially in applications like fleet management. Let’s dive deeper into how these sensors work and what clients need to consider for successful installation.
Sensor Types
There are several types of fuel level sensors, but for this discussion, we’ll focus on resistive-based sensors. These sensors operate based on changes in electrical resistance as the fuel level varies.
Installation Process
a. Sensor Placement
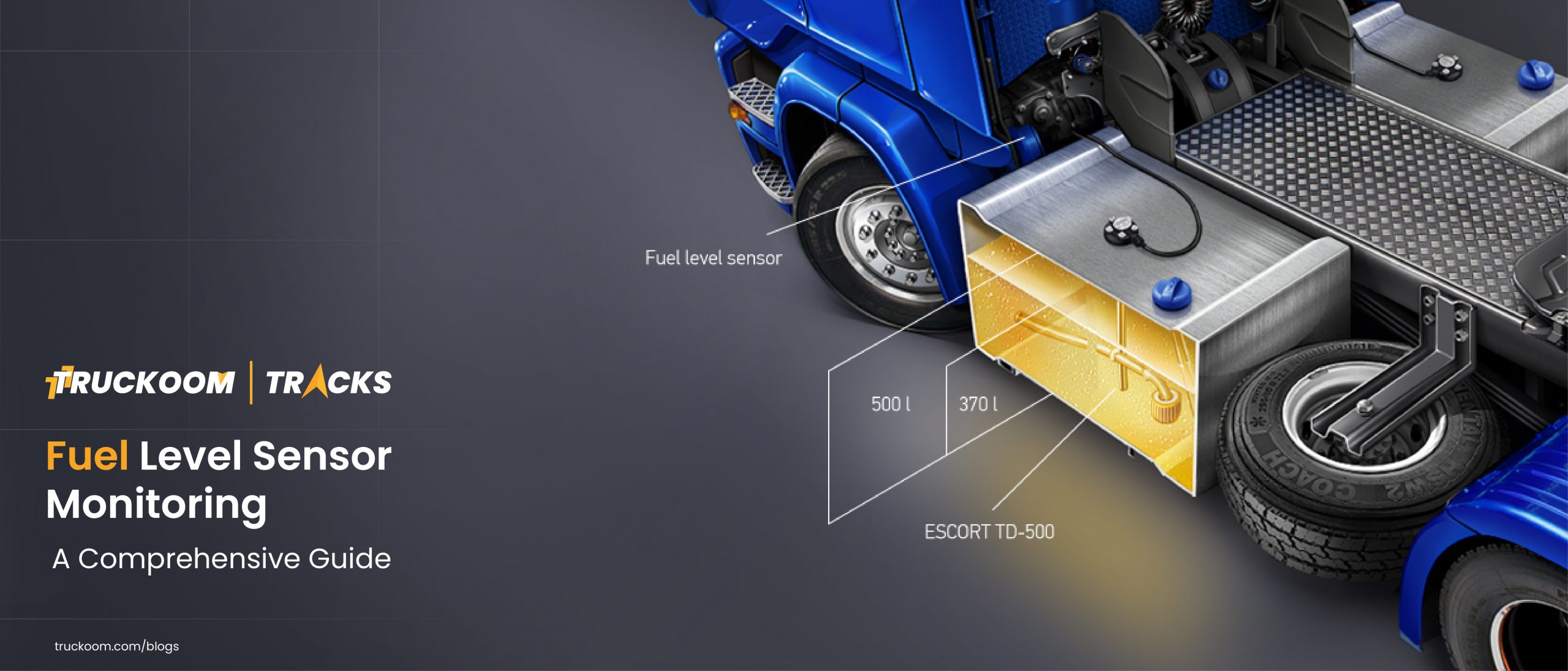
- Inside the Fuel Tank: Fuel level sensors are typically installed directly inside the fuel tank. They can be mounted at various points, such as the top, side, or bottom.
- Calibration: Before installation, the sensor must be calibrated to ensure accurate readings. Calibration compensates for variations caused by factors like tank shape, fuel type, and sensor position.
b. Components Required
- Fuel Level Sensor: The sensor itself, which includes a float mechanism or a conductive rod.
- Wiring Harness: Connects the sensor to the connected GPS device.
- Connector: Provides a secure connection point for the wiring harness.
- Mounting Hardware: Bolts, gaskets, and seals for securing the sensor inside the tank.
How It Works
- Float Mechanism: The sensor’s float moves up and down with changes in fuel level. As the fuel level rises, the float moves upward; as it falls, the float descends.
- Resistance Variation: The sensor’s resistance changes as the float position shifts. This change in resistance corresponds to the fuel level.
- Electrical Signal: The sensor sends an electrical signal (usually a voltage) to the connected GPS device. This signal is proportional to the fuel level.
Calibration and Accuracy
- Initial Calibration: Manufacturers provide calibration instructions specific to their sensors. This involves setting the sensor’s reference points (empty and full) accurately.
- Ongoing Calibration: Regular calibration ensures consistent accuracy. Factors like temperature, fuel quality, and wear can affect readings over time.
Client Considerations
For a successful installation, clients should:
- Choose the Right Sensor: Consider factors like tank shape, fuel type (gasoline, diesel), and compatibility with the vehicle’s system.
- Tank Access: Ensure easy access to the fuel tank for installation and maintenance.
- Quality Fuel: Clean, high-quality fuel minimizes sensor contamination.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically check and recalibrate the sensor to maintain accuracy.
Benefits of Fuel Level Monitoring
Fuel level sensors offer several advantages:
- Cost Savings: Efficient fuel management reduces expenses.
- Theft Prevention: Detect unauthorized fuel usage promptly.
- Maintenance Alerts: Identify irregular consumption patterns.
- Environmental Impact: Optimize fuel usage for a greener footprint.
In summary, fuel level sensors are essential for accurate fuel monitoring. Clients should choose wisely, follow installation guidelines, and prioritize regular maintenance for optimal results.