In the ever-evolving landscape of fleet and transport management, one persistent challenge looms large – the issue of fuel costs. As the lifeblood of any transportation system, fuel plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact of fleets worldwide. In this blog, we’ll explore the multifaceted aspects of the fuel challenge and how it shapes the strategies and decisions of fleet and transport managers.
It’s worth saying that at the beginning of 2021, fuel prices grew more than half a dollar per gallon. The global demand is high, so it won’t likely disappear any time soon. The report by Government Fleet says that fleet operators attribute “fuel price increases, parts, and oil increases, and technology costs” to the main factor that leads to higher operating expenses.
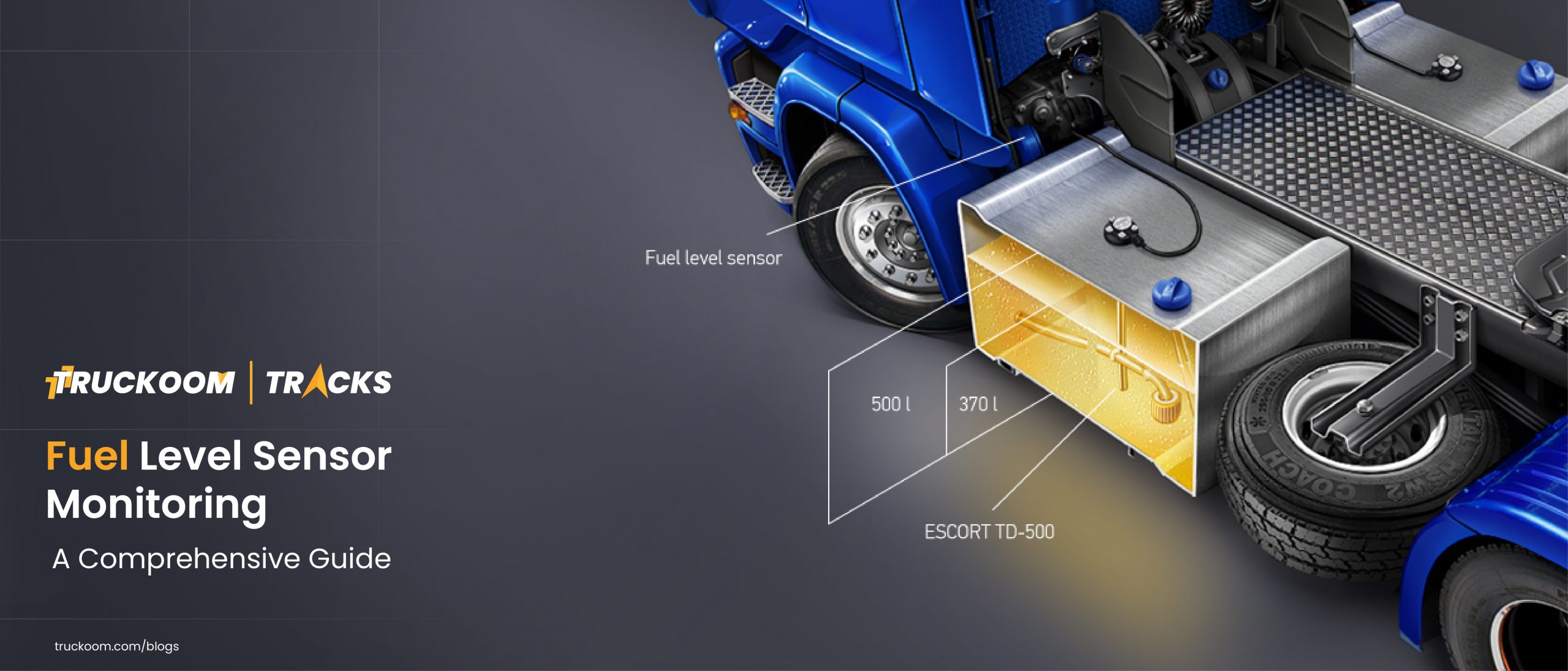
What’s more, every fleet manager knows how challenging and complex this whole process is. Unless you use technology applied to fleet management. A fuel management system (an FMS) combines both hardware and software products. Such systems help maintain, control, and monitor fuel consumption for fleets of any size, so it’s possible to integrate measurement and control processes from fueling a truck to further consumption.
Tracks By Truckoom
Tracks by Truckoom is our leading Fleet management system , our responsibility towards our clients is not to offer them just another GPS solution. Our efforts are aligned with the most important vision of any transporter, which is, how best can we reduce operating costs. And as for any transportation business, often the biggest recurring cost comes from fuel consumption.
Here’s how we have helped our clients save ~20% on average in fuel costs.
- Fuel Consumption Analysis:
Integrated fuel monitoring systems collect data on fuel consumption in real-time. Transporters can analyze this data to identify trends, track variations, and pinpoint anomalies. Such insights help in making informed decisions to improve fuel efficiency and reduce overall fuel costs. - Fuel Theft Prevention:
GPS technology enables transporters to monitor fuel levels remotely. This helps in detecting and preventing fuel theft, a common issue in the transportation industry. By addressing unauthorized fuel usage, transporters can minimize losses and optimize fuel utilization. - Optimized Route Planning:
Improving fuel efficiency is a top priority for fleet and transport managers seeking to optimize operational costs and reduce their environmental footprint. Route optimization software, and telemetry systems play a pivotal role in maximizing the miles covered per gallon. . With accurate GPS data, transporters can analyze historical travel patterns and identify the most fuel-efficient routes, and unnecessary deviations, for their vehicles. By optimizing routes, transporters can minimize unnecessary mileage and reduce fuel consumption, ultimately leading to significant cost savings. - Monitoring Driving Behavior:
Human factors, particularly driver behavior, significantly impact fuel efficiency. Fleet managers are increasingly investing in driver training programs to promote fuel-conscious driving habits. Strategies include reducing idling time, maintaining proper tire pressure, and optimizing acceleration and deceleration patterns. These behavioral changes can contribute significantly to fuel savings over the long term. GPS-based systems can track driver behavior, including speed, idling time, and harsh acceleration or braking. By promoting and incentivizing fuel-efficient driving habits, transporters can reduce fuel wastage. - Preventive Maintenance:
GPS-based fuel monitoring can integrate with vehicle diagnostics to provide alerts for maintenance needs. Regular maintenance, such as timely oil changes and engine tune-ups, ensures that vehicles operate at peak efficiency, reducing fuel consumption and preventing costly breakdowns. - Customized Reporting:
Transporters can generate customized reports based on the data collected from GPS-based fuel monitoring systems. These reports can offer a detailed analysis of fuel usage, driver performance, and operational efficiency, enabling transport managers to identify areas for improvement and implement targeted strategies.

Conclusion
Fuel management in fleet and transport operations is a dynamic and multifaceted challenge that requires a focused approach. Fleet managers must continuously adapt to navigate the complexities of fuel-related issues. As the industry evolves, staying ahead of the curve in fuel management will not only drive operational efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient future for fleet and transport management.
Saving costs and save the environment by getting Tracks by Truckoom today!